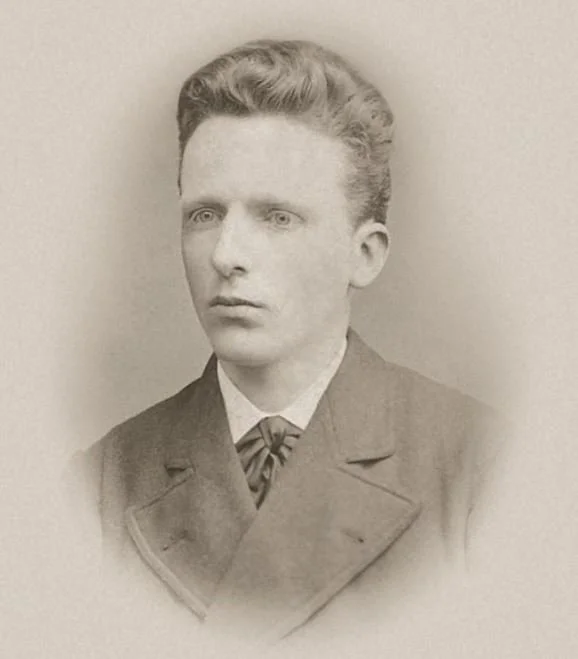
How Wealthy was Vincent van Gogh?
Van Gogh - Self-Portrait with Dark Felt Hat, 1886
Vincent van Gogh is one of the most celebrated and influential artists of all time. His vibrant brushstrokes, expressive landscapes, and haunting self-portraits have captivated audiences for decades. However, behind the artistic brilliance lies a common perception that Van Gogh was a perpetually struggling and impoverished artist, barely making ends meet during his lifetime.
This narrative has romanticised the image of a tortured genius, toiling away in obscurity, with little financial recognition or stability. But is this portrayal a true reflection of Van Gogh's financial reality? In this article, I delve deeper into the life of Vincent van Gogh to explore the financial situation and challenge the commonly held beliefs about his poverty.
Van Gogh’s Early Life and Background
Vincent van Gogh was born in the Netherlands to a middle-class family. His father, Theodorus van Gogh, was working as a minister, and his mother, Anna Cornelia Carbentus, came from a family of art dealers. Van Gogh was the eldest of six children, and his upbringing was influenced by a blend of religious and artistic influences.
Van Gogh’s Father, Theodorus van Gogh
During his childhood, Van Gogh exhibited a strong affinity for drawing and sketching. However, his early career aspirations took him down a different path. Following in the footsteps of his uncles, he briefly pursued a career as an art dealer in the renowned Goupil & Cie gallery in The Hague and later in Paris and London. This experience allowed him to develop an understanding of the art market and gain exposure to various artistic styles and movements.
Despite working in the art trade, van Gogh’s true passion lay in creating art rather than selling it. Over time, he made a significant transition from being an art dealer to pursuing his own artistic endeavours. This decision marked a pivotal point in his life, as he fully committed himself to becoming an artist.
Van Gogh’s journey towards becoming an artist was not without challenges. His early artistic attempts were marked by experimentation and a search for his unique style. He sought inspiration from various sources, including Dutch realist painters, Japanese woodblock prints, and the vibrant colours of the Impressionist movement.
Throughout this period, van Gogh faced financial difficulties, often relying on the support of his family. His parents and siblings, particularly his brother Theo, played a crucial role in providing both emotional and financial assistance, enabling him to focus on his artistic pursuits. It was Theo who remained a steadfast supporter and confidant throughout Van Gogh’s life, particularly as he grappled with mental health issues.
The early life and background of Vincent van Gogh laid the foundation for his artistic journey. From his upbringing in a middle-class family to his experiences as an art dealer, these formative years shaped his perspective and ignited his creative spark. The transition from art dealer to artist was a significant turning point, and the support of his family would prove invaluable in his pursuit of artistic greatness.
Financial Support from Family
Van Gogh’s family played a crucial role in supporting his artistic ambitions throughout his life. They provided both financial assistance and emotional support, allowing him to focus on his artistic pursuits and navigate the challenges he encountered along the way.
Theo Van Gogh, 1878
One of the most significant figures in Van Gogh’s life was his younger brother Theo.
Theo, who also worked in the art industry as an art dealer, became Vincent’s confidant and primary source of support. Theo believed wholeheartedly in Vincent’s talent and artistic vision, providing unwavering encouragement and financial aid to him.
Theo’s financial support was instrumental in allowing Van Gogh to focus on his art without the burden of financial worries. He provided Vincent with a regular allowance, enabling him to afford art supplies, pay for living expenses, and even finance occasional travel.
Beyond the financial aspect, Theo’s emotional support was equally vital to Van Gogh’s well-being and creative journey. They shared a deep bond, exchanging letters filled with discussions on art, literature, and personal struggles. Theo’s understanding and empathy provided Van Gogh with a sense of solace and strengthened his resolve during times of artistic self-doubt and emotional turbulence.
While Theo played a central role in supporting Van Gogh, other family members also contributed to his artistic endeavours.
Van Gogh’s parents, Theodorus and Anna, recognised their son’s passion for art and, although initially skeptical, eventually embraced his artistic ambitions. They provided support in various forms, including moral encouragement and occasional financial assistance when they were able to do so.
Van Gogh’s sister Willemien also showed support for his artistic career. They exchanged letters, discussing artistic techniques and sharing their perspectives on the art world. Although her contributions may not have been as substantial as Theo’s, her support further reinforced Van Gogh’s determination and sense of belonging within the family unit.
The financial and emotional support provided by Van Gogh’s family allowed him to pursue his artistic vision despite the financial challenges he faced throughout his life. Without the backing of his family, Van Gogh’s artistic journey may have encountered even greater obstacles.
Artistic Career and Financial Struggles
Vincent van Gogh’s artistic career went through a remarkable evolution, encompassing various artistic phases and styles. However, alongside his artistic pursuits, Van Gogh faced persistent financial struggles that significantly impacted his life and work.
Van Gogh’s artistic journey began with his early experiments in the Netherlands, where he primarily focused on dark and sombre subjects, influenced by Dutch realist painters such as Jean-François Millet and Jules Breton. During this period, he faced challenges in selling his paintings, which limited his financial stability.
In 1886, Van Gogh moved to Paris, seeking artistic inspiration and exposure to new artistic movements. He became acquainted with the Impressionists and Post-Impressionists, which influenced his own style.
Despite his growing artistic development, Van Gogh struggled financially. He relied heavily on the financial support provided by his brother Theo, as his own art sales were insufficient to sustain him.
In 1888, Van Gogh made a pivotal decision to move to Arles in the south of France. It was during this period that he created some of his most iconic works, including “Sunflowers”. However, financial difficulties continued to plague him. Van Gogh’s correspondence with Theo reveals his constant concerns about money, often expressing his inability to afford basic necessities.
Still Life: Vase with Fifteen Sunflowers, 1889
Van Gogh’s financial struggles also impacted his mental health. The stress of his precarious financial situation, coupled with personal setbacks and artistic challenges, took a toll on his well-being. His mental health deteriorated, leading to episodes of severe depression and anxiety.
Specific instances highlight Van Gogh’s financial difficulties. In Arles, he experienced a significant financial setback when his friend and fellow artist Paul Gauguin decided to end their collaborative living arrangement. This sudden change put a strain on Van Gogh’s finances and further exacerbated his emotional turmoil.
In 1889, Van Gogh voluntarily admitted himself to a psychiatric hospital in Saint-Rémy-de-Provence. During this time, he continued to produce art, but his financial situation remained dire. He relied on the financial support and encouragement from Theo to sustain him through this challenging period.
The Starry Night, 1889
Van Gogh’s financial struggles ultimately contributed to his decision to move to Auvers-sur-Oise, where he hoped to find stability and continue his artistic pursuits. However, tragically, his life was cut short when he died in 1890.
His financial struggles became an integral part of his artistic narrative, reflecting the passion, dedication, and resilience that defined his artistry.
Sales and Recognition during Van Gogh’s Lifetime
During Vincent van Gogh’s lifetime, his artistic recognition and sales were relatively limited compared to the widespread acclaim he would later receive. However, there were key patrons, collectors, and exhibitions that played a significant role in supporting his art financially and laying the foundation for his posthumous success.
Theo van Gogh: The most crucial supporter of Vincent’s art was his brother Theo. As an art dealer, Theo introduced Vincent’s work to potential buyers and collectors. He tirelessly promoted Vincent’s paintings, striving to generate sales and secure commissions. Theo’s belief in his brother’s talent and unwavering support allowed Vincent to continue his artistic pursuits.
Johanna Gezina van Gogh-Bonger: Theo van Gogh’s wife Johanna Gezina van Gogh-Bonger, played a significant role in Vincent’s posthumous fame. After Vincent’s death, Johanna inherited his letters and paintings from Theo, who died just six months after Vincent. She worked tirelessly to promote Vincent’s art and letters. Johanna also organised exhibitions of Vincent’s work, including one of the first solo exhibitions of Vincent'‘s art in Amsterdam in December 1892.
Paul Gauguin: While their cohabitation in Arles ended abruptly, Gauguin’s support and artistic collaboration had a notable impact on Van Gogh’s artwork. Their artistic exchange and mutual influence helped shape van Gogh’s style and contributed to the development of his unique artistic expression. Though Gauguin did not provide substantial financial support, their interactions as artists influenced Van Gogh’s creative journey.
Émile Bernard and Louis Anquetin: Both Bernard and Anquetin were fellow artists who formed part of the avant-garde art scene in Paris. Their friendship and artistic camaraderie provided Van Gogh with a supportive network. They admired his work, promoted his art within their circles, and contributed to the recognition of his talent.
Gustave Caillebotte: Caillebotte, a fellow artist and collector, purchased some of Van Gogh’s paintings. His patronage not only provided financial support but also helped to establish Van Gogh’s reputation within the artistic community.
Les XX Exhibition: Van Gogh’s work was included in the prestigious Les XX Exhibition in Brussels in 1890. This exhibition introduced his art to a broader audience, generating critical attention and interest. Although Van Gogh did not achieve significant sales from this exhibition, it marked a milestone in terms of exposure and recognition.
There is a myth that Van Gogh only sold one painting during his lifetime, “The Red Vineyard”. However, Vincent van Gogh is known to have sold or bartered a number of paintings during his lifetime, sometimes with other artists, and sometimes in exchange for food or drawing and painting supplies. He even gave paintings away from time to time for various reasons. Evidence also shows that his brother Theo sold one of his self-portraits to an art dealer in London in 1888, so he sold more than one painting during his lifetime.
It is important to note that Van Gogh’s recognition and sales during his lifetime were modest, and he experienced more financial difficulties than financial success.
The widespread acclaim and commercial success he enjoys today came posthumously, driven by the efforts of Theo, and Theo’s wife, Johanna Gezina van Gogh-Bonger, who both dedicated themselves to promoting Vincent's work after his untimely death.
Posthumous Fame and Value of Van Gogh's Works
The posthumous recognition and skyrocketing value of Vincent van Gogh’s artworks are a testament to the enduring power and impact of his artistic legacy. While Van Gogh faced financial struggles during his lifetime, his paintings now command astronomical prices and are cherished by art collectors and museums worldwide.
After Theo van Gogh’s death in 1891, Johanna van Gogh-Bonger, his widow, took on the task of curating and promoting Van Gogh’s artworks. Through her efforts, Van Gogh’s paintings began to be exhibited and published, gaining critical acclaim and public attention.
In 1911, Van Gogh’s works were included in the groundbreaking “Sonderbund” exhibition in Cologne, Germany. This exhibition showcased the works of avant-garde artists, including Van Gogh, and played a significant role in raising awareness and appreciation for his art.
Van Gogh’s posthumous fame reached new heights in the 20th century, with his works becoming highly sought-after by art collectors. Major sales and auctions of his paintings have consistently set records and established Van Gogh as one of the most valuable artists in history.
Some notable sales and acquisitions include:
Orchard with Cypresses, 1888
“Orchard with Cypresses” (1888): - Sold for $117.2 million in 2022 at Christie’s New York.
“Labourer in a Field” (1888): - sold for $81 million in 2017 at Christie’s New York
“Portrait of Dr. Gachet” (1890): In 1990, this iconic painting was sold at auction for a staggering $82.5 million.
“Irises” (1889): In 1987, this vibrant floral masterpiece fetched a record-breaking price of $53.9 million.
“Sunflowers” series: Several paintings from Van Gogh’s celebrated “Sunflowers” series have been sold for large amounts, with the most notable being a sale in 1987 for $39.9 million.
The increasing value and market demand for Van Gogh’s works reflect the profound impact his art has had on the art world and popular culture. His unique style, emotional depth, and ability to capture the essence of human existence continue to resonate with audiences worldwide.
Today, Van Gogh’s paintings are not only admired for their artistic brilliance but also revered as cultural treasures. The enduring fascination with his art has solidified Van Gogh’s status as a visionary artist, and his works continue to inspire and captivate art enthusiasts and collectors alike.
Legacy and Cultural Impact
Vincent van Gogh’s artistic legacy extends far beyond the realm of traditional art appreciation.
His style, emotional depth, and unique approach to capturing the essence of human existence have had a profound impact on the art world and continues to inspire, influence, and resonate with audiences today. His legacy can be seen in:
Artistic Influence: Van Gogh’s bold use of colour, expressive brushwork, and emotional intensity revolutionised the art world and paved the way for subsequent artistic movements. His influence can be seen in the works of Expressionists, Fauvists, and even contemporary artists.
Popular Culture: Van Gogh’s art has transcended the confines of the art world, permeating popular culture in various forms. His iconic paintings, such as “The Starry Night” and “Sunflowers”, have been reproduced, parodied, and referenced in countless films, advertisements, music videos, and even fashion.
Museums and Exhibitions: The establishment of dedicated museums, such as the Van Gogh Museum in Amsterdam, the Kröller-Müller Museum in Otterlo, Netherlands, and the Musée d'Orsay in Paris, showcases the enduring cultural impact of Van Gogh’s art. These institutions attract millions of visitors annually, offering them the opportunity to engage with his paintings firsthand and gain a deeper understanding of his artistic journey.
Art Market and the Van Gogh Brand: Van Gogh’s posthumous fame and the commercialisation of his art have given rise to the “Van Gogh brand”. The popularity of his works has been capitalised upon through licensing agreements, merchandising, and reproductions.
The financial implications of the Van Gogh brand have been substantial. The high demand for his paintings, coupled with limited availability, has led to remarkable auction prices and art market transactions. The value of Van Gogh’s works has soared, making them highly coveted by collectors and investors alike.
Vincent van Gogh’s legacy is not solely defined by financial implications or commercial success but rather by his ability to create art that resonates with the depths of human emotion and captures the essence of the human experience.
Misconceptions and Myth of Van Gogh’s Poverty
Vincent van Gogh is often depicted as the quintessential struggling and impoverished artist, perpetuating a common narrative that has become deeply ingrained in popular culture.
However, upon closer examination, it becomes evident that the perception of Van Gogh’s poverty is oversimplified and, in some cases, misguided. Challenging these misconceptions provides a more nuanced understanding of Van Gogh’s financial situation and the complexities of his life.
Financial Support from Family: One of the primary misconceptions is that Van Gogh was entirely destitute throughout his life. While he did face financial challenges, he received substantial support from his family, particularly his brother Theo. This support significantly alleviated the financial burden on Van Gogh.
Art Market and Sales: Contrary to popular belief, Van Gogh did sell some of his paintings during his lifetime. Although the number of sales was relatively limited, they did contribute to his financial well-being to some extent.
Theo’s Art Business: Theo van Gogh’s role as an art dealer and his connection to the art market provided him with insights, networking opportunities, and a platform to promote his brother’s art.
Voluntary Simplicity: Van Gogh’s lifestyle choices also contributed to the perception of his poverty. He willingly embraced a simple and frugal existence, often prioritising his art over material possessions. Van Gogh’s focus on his artistic pursuits and his rejection of conventional societal expectations of success may have influenced the perception of him as a destitute artist.
Mental Health Challenges: Van Gogh’s mental health struggles further complicated his financial situation. Episodes of depression and anxiety impacted his ability to maintain consistent employment or engage in conventional income-generating activities.
By challenging the prevailing misconceptions surrounding Van Gogh’s poverty, we can appreciate the multifaceted nature of his existence and the extraordinary artistic contributions he made despite the challenges he faced. Van Gogh’s story serves as a reminder that the true value of an artist’s work extends beyond monetary measures and should be appreciated for its artistic merit and enduring impact on the world of art.
I have also provided more information about where to view Van Gogh paintings in Europe, California, New York, Chicago, Washington D.C. and New England. For more articles about Vincent van Gogh, click here.
I have written other articles about where to view Frida Kahlo artworks and Gustav Klimt artworks, that you may also find interesting.
I hope you have found this article about Vincent van Gogh interesting. I would love to hear your thoughts, please feel free to email me at sarahransomeart@gmail.com.
If you enjoyed this blog post, you might like…
BLOG TOPICS
- July 2025
- December 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- October 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021